Where are We in the Process Cycle?
This part of the PPP Guide covers management of the contract during the Construction Phase of the PPP life cycle (delivery of the asset up to and including the commissioning of the asset). Therefore, all the general issues discussed previously in this chapter will apply. However, certain activities that are only relevant to the Construction Phase are discussed in more detail below. Box 7.5a and 7.5b deal with the learning objectives of this part of the PPP lifecycle.
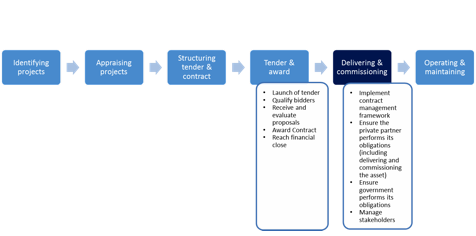
In the previous phase, the tender was launched (through a Request for Qualification [RFQ] stage or by directly issuing a Request for Proposal [RFP] in some jurisdictions), bidders were qualified, proposals were received and evaluated, the contract was awarded, and financial close was achieved.
In this phase, the private partner delivers and commissions the different components of the project. The government implements its contract management framework, ensures that both the private partner and government perform their obligations, and manages stakeholder interfaces. See figure 7.4.
At the end of this phase, the project reaches the Operations Phase in which the infrastructure is operated and maintained to deliver services to users.
FIGURE 7.4: Where We are in the Process Cycle
|
BOX 7.5a: Objectives – Construction Phase The objectives of contract management in the Construction Phase are as follows.
|
|
BOX 7.5b: Learning Objectives for Part B This section will allow the reader to understand the following concepts:
|


Add a comment